- 接合関連
低温実装可能な異方性導電膜の特徴とその用途
異方性導電膜(ACF)の低温実装
デクセリアルズの接合ソリューションである異方性導電膜(ACF)は、液晶ディスプレイや有機ELディスプレイ、マイクロLEDディスプレイなどへのICやFPCの実装のほか、カメラモジュールやタッチパネル、ICカードなどへの部品搭載に活用が広がっています。その主な理由は、低温実装が必要なケースに対応できることにあります。

プリント基板や電子部品の中には、構成材料の性質上、150℃以上の高温に耐えられないものや、高温で特性を維持できないものがあります。例えば、静電容量タッチセンサーに使われるITO膜(透明導電膜の一種)を回路層とするCOP(シクロオレフィンポリマー)基板やハプティクス(触覚伝達)モジュールに使われるピエゾ素子(圧電素子)、小型カメラモジュール内のポリカーボネートなどのプラスチック製レンズ、ICカードなどに使われる融点が150℃以下のPETなどのフィルム基材などです。これらの材料・部品は、高温に曝されると特性が変化することから、部品実装・部品固定を低温で行う必要があります。
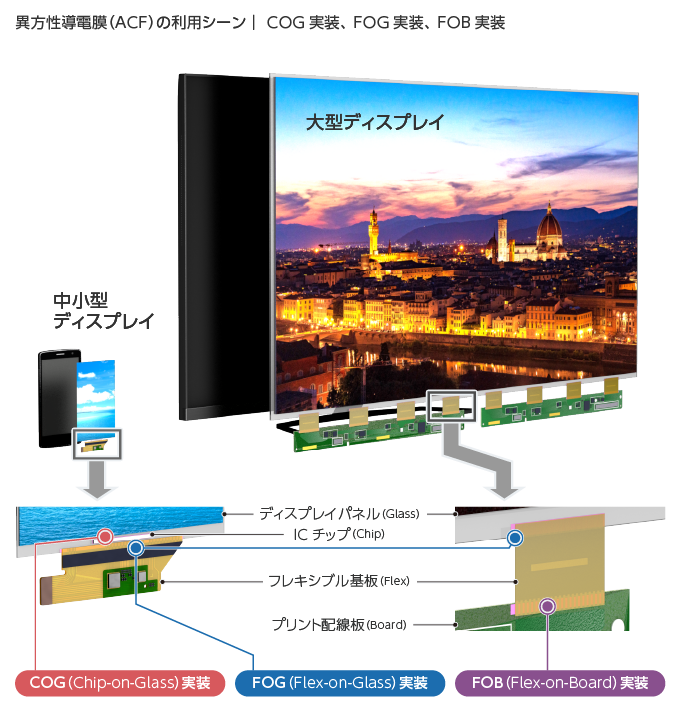
一方で、フィルム基材に配線を印刷するプリンテッドエレクトロニクス技術が注目されています。これは、フィルムなどの基材の上に電気配線やセンサーなどの電子回路を印刷して、直接形成する技術です。
従来の基板製造では、エッチングに代表されるサブトラクティブ法(不要部分を取り除いていく工法)が回路形成の主流です。この工法では、取り除くために光の照射(露光)や化学薬品、水を使うことから多くのエネルギー、リソースを消費します。また、取り除いた物質の多くは廃棄されます。これに対しプリンテッドエレクトロニクスは、回路となる材料を所定位置に必要量印刷するため、比較的無駄の少ない工法であり、環境負荷やCO2排出量の低減が図れると言われています。フィルム基材の多くは耐熱性に問題があるため低温実装可能なACFは、こうしたプリンテッドエレクトロニクスにも適しています。
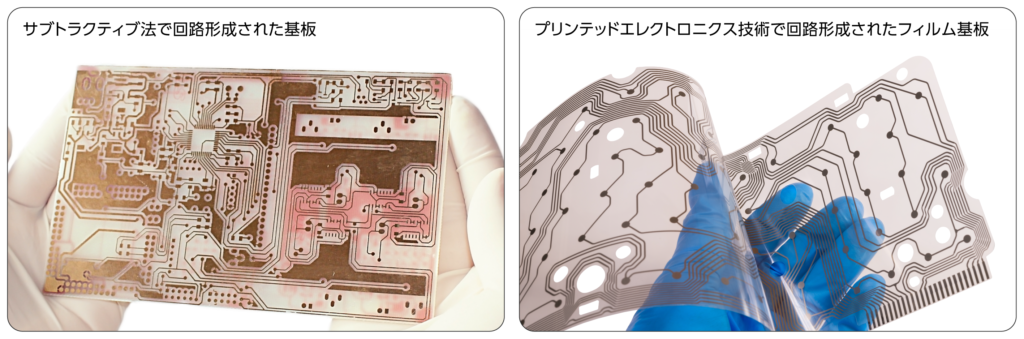
ACF本圧着後のリワーク/リペア
フレキシブル回路基板(FPC)と基板(PCBやガラス基板)を実装する用途において、ACF実装後にリワークやリペアを行う可能性がある場合には、アクリル樹脂を使ったACFの使用が推奨されます。ただし、リワークやリペア自体を推奨しているわけではありません。部品製造の工程に組み込む際には、事前にリワーク製品・リペア製品を使った信頼性評価などを行って当該製品に品質上の問題が発生しないことを確認した上で実施されることを推奨しています。
本実装後のリワークやリペアでは、通常、ヒートガンや工業用アイロンを使って局所(ACF実装部)加熱し、FPCを剥がします。その後、基板上の配線間に残った硬化樹脂を、MEK(メチルエチルケトン)やNMP(N-メチル-2-ピロリドン)などの溶剤を使って綿棒で丁寧に除去します。この際、FPCはカール(反り変形)してしまうことが多く、配線間の樹脂残渣の除去は難しいため、FPC自身の再利用は推奨されません。ワークやリペアは、アクリル系ACFの使用により可能ですが、製品品質を高いレベルに保つためにも、できる限り避けることが望まれます。
低温硬化・常温保管可能な熱可塑性ACF
ACFには一般的なエポキシやアクリル系の熱硬化性樹脂製品のほか、熱可塑性樹脂で構成された製品もあります。
高い温湿度環境(加速試験条件:85℃/85%RH、500時間)での高い信頼性(機能維持)が求められる用途では熱硬化性ACFを推奨していますが、使用環境がそこまで厳しくない場合、110℃付近で接合可能で使い勝手の良い熱可塑性ACFが選択肢として入ってきます。
はんだ、コネクター代替向けFilm On Board/Film用異方性導電膜(ACF)
熱硬化性ACFでは通常5℃以下の冷蔵保管が必要で、製造後5〜7カ月の使用期限がありますが、熱可塑性ACFは常温で製造後2年という長期保管ができます。また、はんだ接合用圧着装置など簡易的な熱圧着装置での接合も可能なため、ACF実装専用の装置導入の必要がなく、投資コストを抑えられます。こうした熱可塑性ACFは、ICカードのような一般使用環境の用途で利用されています。
ICカード向け異方性導電膜(ACF)の特長とメリット
IoTやプリンテッドエレクトロニクスの発展に伴い、自動車、ヘルスケア、産業機器など、さまざまな分野でACFの採用を検討される機会が増えています。デクセリアルズでは、多種多様な産業分野での低温実装のご要望に合わせて製品を提案させていただいております。ぜひお気軽にお問合せください。
関連記事

私たちデクセリアルズはデバイスの進化に欠かせない材料や次世代のソリューションを生み出す、マテリアルメーカーです。
電子部品、接合材料、光学材料をはじめと世界中のパートナーと新しい価値を生み出していきます。
- SHARE
当社の製品や製造技術に関する資料をご用意しています。
無料でお気軽にダウンロードいただけます。
お役立ち資料のダウンロードはこちら
当社の製品や製造技術に関する資料をご用意しています。
無料でお気軽にダウンロードいただけます。
お役立ち資料のダウンロードはこちら