- 電子部品関連
世界に広がる「電動バイク」とその安全性(バッテリーと二次保護ヒューズ)
目次
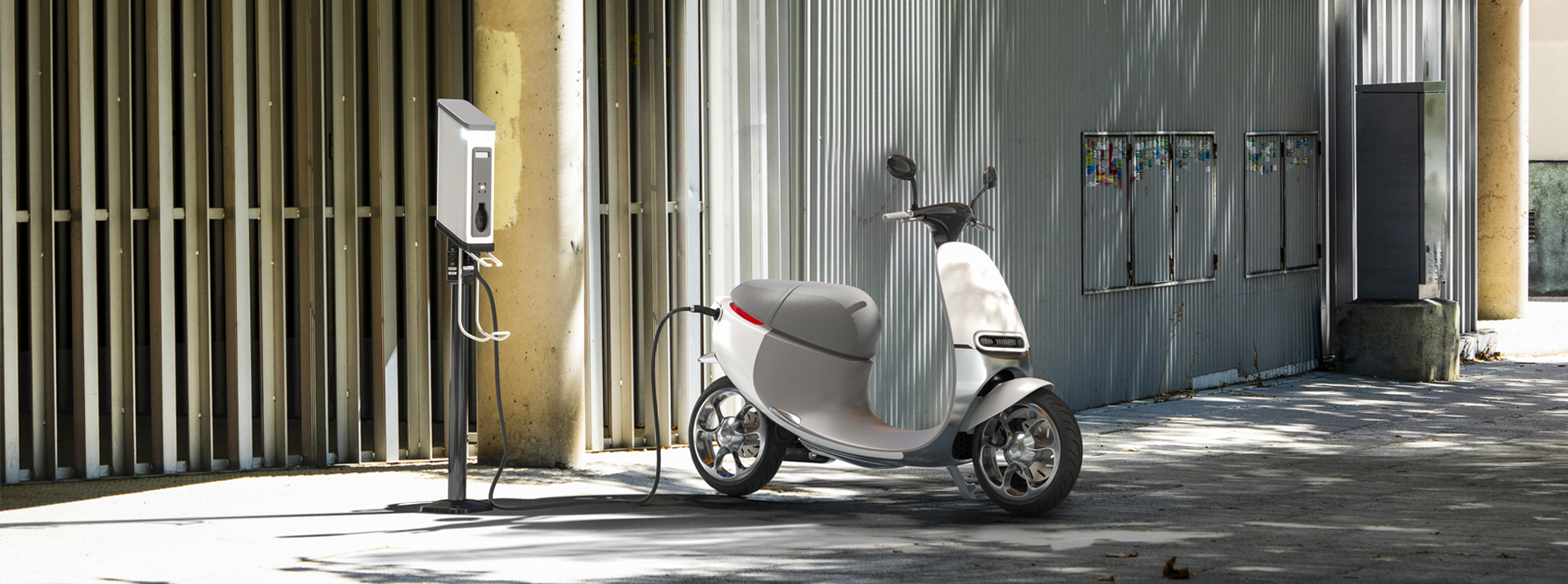
世界で急拡大する電動バイク市場
今、急速に電動バイクや電気自動車の普及が始まっています。皆さんの中にも、乗ったことがある方がいらっしゃるのではないでしょうか。SDGsや環境負荷の低減が叫ばれる現代社会において、走行中や停車中に排気ガスを出さない電気自動車や電動バイクは、環境負荷の低い移動手段として世界から注目を集めています。
電動バイクのメリットとデメリット
電動バイクとは電気で動くバイクです。通常のバイクはガソリンを燃料にエンジンを動かしますが、電動バイクは充電式バッテリーからモーターに電気が供給され、モーターの動力により動きます。近年は環境負荷を低減する意識の高まりから、電気自動車が次世代の自動車として注目され、広く普及するようになりました。電動バイクも電気自動車と同様に、ガソリンで動くバイクの代わりに、環境にやさしく、乗りやすい乗り物として市場の成長が期待されています。
エンジンバイクと電動バイクの違いは大まかには以下の通りです。
| エンジンバイク | 電動バイク | |
|---|---|---|
| 排気ガス | 排出する | 排出しない |
| 騒音 | あり | なし |
| ランニングコスト(燃費・電費) | 高くはない(1度の給油で原付の場合、数百円) | より安い(1回の充電で100円以下) |
| 航続距離 | 原付の場合、1度の給油で数百km | 1回の充電で数十km |
| 補給 | ガソリンスタンドで給油 | 自宅の室内の充電器で充電(交換式を除く) |
| 給油・充電 | 数分かかる | 数時間かかる(交換式を除く) |
搭載されているリチウムイオンバッテリーのモデルや定格電圧により異なりますが、電動バイクの充電は、残量がゼロの状態からフル充電状態になるまでに、数時間がかかります。大きなメリットはそのランニングコストです。充電時にかかる電気代はモデルにもよりますが、およそ数十円程度とガソリンに比べて圧倒的に安くなります。エンジンバイクが数分で給油できる点に比べると、充電にかかる時間が長いのがデメリットですが、ランニングコストはかなりおさえられます。
電動バイクの種類
電動バイクは、街乗りに適したスクータータイプのモデルが最も多く販売されています。その一方で、最高速度や航続距離を大幅に伸ばした電動バイクも欧州メーカーから発売されており、本格的なツーリングが楽しめる電動バイクの普及も広がっています。
また、電動バイクには、コンパクトに折りたためる、持ち運びに便利なタイプもあります。そうした折りたたみ型電動バイクは、軽自動車やワンボックスカーなどに収納して運ぶことができ、旅行先での短距離の移動手段など、さまざまな利用シーンが考えられます。
さらに、「ペダル付き電動バイク」と呼ばれる電動バイクも登場しており、「モーター」「ペダル」「モーターとペダル」と3通りの動力でバイクを運転することができます。バッテリーが切れても、ペダルを踏むことで通常の自転車のように移動できることが利点です。モーターがアシストしてくれる2輪の乗り物には「電動アシスト自転車」がありますが、電動自転車の場合は、ペダルを漕がなければ動きません。それに対して「ペダル付き電動バイク」は、ペダルを漕がずとも一定のスピードでバイクのように進むことができることから、道路交通法で「原動機付自転車」に定められており、乗るのには原付免許が必要となります。
電動バイクへの搭載が進むリチウムイオンバッテリー
これらの電動バイクで幅広く使われているのが「鉛バッテリー」です。鉛バッテリーは製造コストが安く、繰り返しの充電にも強いため、電動バイクで幅広く採用されています。一般的な構造として、プラス極、マイナス極に鉛や鉛の合金板を使用し、電解液に希硫酸が使用されています。コストが安いことから低価格の電動バイクでは鉛バッテリーが採用されるケースが多いですが、容積が大きく、重量があるというデメリットがあります。
そのため近年では、高価格帯の電動バイクを中心にリチウムイオンバッテリーが採用されるモデルが増えています。リチウムイオンバッテリーはノートPCやスマートフォンなどの小型モバイルIT機器には必ず採用されており、私たちの生活にもとても身近なバッテリーです。リチウムイオンバッテリーは、鉛バッテリーと比較して、小型・軽量かつ、高電圧という大きな特長があります。同体積、同重量での電池容量を示すエネルギー密度で比較すると、リチウムバッテリーは鉛バッテリーに比べて非常に高い値を示します。

なお、バッテリーの充電方法には普通充電と急速充電がありますが、急速充電を繰り返すとバッテリーへの負担が大きくなり、バッテリー寿命が短くなる傾向があります。そのため、各社の電動バイクではバッテリーの種類や特性に合わせて負荷の少ない充電方法を取っています。
電動バイクのジレンマとバッテリーの改良
環境負荷低減という点で、主にアジアで普及が期待される電動バイクですが、バイクの電動化には「ジレンマ」もあります。
電気で動く電気自動車や電動バイクで、もっとも重視される指標の一つが航続距離です。近年のEVとガソリンエンジン自動車を比較しても、EVの航続距離は順調に伸びており、300km-400km程度の航続距離の電気自動車が出てきています。一方、電動バイクは1回の充電での航続距離は40km(1名乗車時)程度に過ぎません。同じタイプの160ccガソリンタイプのバイクが一回の給油で400km以上走行可能であるのに比べて、10分の1の距離しか走れないという大きな差があります。
前述のように、電動バイクの航続距離に大きな影響を及ぼすのは、バッテリーの容量およびバイク本体とバッテリーを含めた重量です。大容量のバッテリーを搭載することで航続距離は長くできますが、バッテリーそのものの重量によって車重は増えます。車重が増えれば、その分、航続距離は短くなってしまうため、航続距離を伸ばすために大容量のバッテリーを積めば積むほど重量が増えて航続距離が短くなるというジレンマがあるのです。
EVでも同様のジレンマがありますが、車体のフレームに炭素繊維強化プラスチックを採用することで軽量化を図るといった解決策がとられています。一方で、電動バイクでは元々の本体サイズが小さく、車重がそれほど重くないため、車体に軽量素材を使用したとしても軽量化には限界があります。またバイクは車体が小さいことから、バッテリーを搭載できるスペースも限られます。つまり、電動バイクの航続距離がガソリンタイプのバイクに肩を並べるためには、バッテリーの性能向上が不可避となるのです。
その一方で、現在の電動バイクも、例えば、配送ルートがある程度固定されている配達・配送などの用途であれば、限られた航続距離の中で活用することができます。実際に新聞配達や郵便局などで電動バイクが導入されている事例があり、特に深夜や早朝に業務をおこなうことの多い新聞配達では、電動バイクの静音性が評価されています。

また、電動アシスト自転車のようにバッテリー交換が可能なカートリッジ式が採用されている電動バイクであれば、もし充電残量が少なくなっても、バッテリーを交換すれば走行を継続することができます。クルマ(EV)のバッテリーは重量が重く、ユーザーが自力で交換するのは不可能ですが、電動バイクの小型軽量なバッテリーであれば、ユーザー自身の手による交換が可能です。
世界各国の電動バイク市場の現状と未来
視点を世界市場に移すと、電動バイクの状況は、国や地域ごとに大きく異なっています。まず、ガソリン車も含めた自動二輪車の世界販売台数は、主要国を中心として年間に5300万台程度、需要としては4770万台程度というデータがあります。このうち、全需要の実に70%以上が、人々が日常の移動手段としてバイクを使用するアジアを中心とした国々です。中国はこのうち、1780万台程度を占めると言われており、世界最大の自動二輪車市場を形成しています。また、インドもほぼ同等の1770万台規模の生産台数です。インドネシアが580万台、ベトナムが320万台、タイが230万台と続きます。パキスタン、ブラジル、タイも100万台以上生産しているといわれています。一方、日本や北米などでの需要はそれほど高くなく、日本は年間40万台以下、北米でも年間60万台程度といわれます。
この台数のうち、電動バイクがどれぐらいを占めるかというと、中国では年間販売台数が約300万台程度、インドでは14〜15万台程度となっています。インドネシアでは国家として2030年に1300万台以上の電動二輪車保有を目指しており、普及に力を入れています。他にもアジアの各国がCO2排出削減などを目的に、電動バイク導入に向けた法規制や目標を設定しています。
例えば、今後、電動バイク市場の大きな成長が期待されているインドでは、環境問題への関心の高まり、政府の政策、ガソリン価格の高騰、充電インフラの改善、EVで使われる部品生産の現地化やコスト削減によるバッテリー価格の低下などが、普及促進のドライバーとなるとみられています。また、普及の障害としては航続距離に対する懸念や充電時間が長い点、充電インフラの地方部での普及率の低さ、加速性能や速度性能に対する懸念、バッテリー交換コストが高い点などが挙げられています。
こうした市場の状況に対して、各国のバイクメーカーや部品サプライヤーは技術開発を続けており、特に、バッテリー関連技術の開発が続いています。先述の通り、電動バイクは航続距離を伸ばすことが容易でないため、バッテリー交換可能なシステムが検討されています。また、バッテリーに互換性を持たせたり、大容量化、耐劣化性や耐振動性、耐衝撃性の向上、バッテリーの規格を合わせてシェアリングサービスを展開したりするなどといった動きもあります。さらに、国によっては、各家庭に電気を供給する電力系統に電動バイクをつなぎ、余剰電力で充電することで電力系統の負荷を下げ、ピークシフトを実現することで再生可能エネルギーの拡大を進める手段にすることも検討されています。
電動バイクとデクセリアルズのSCP
このように急激に伸長する電動バイク市場ですが、そのバッテリーの安全性を担保する部品として同時に需要が大きく高まっているのが、デクセリアルズの「大電流用セルフコントロールプロテクター(SCP)」です。
ノートPCやスマートフォン、タブレットPCなどに用いられるのは4V〜12V程度の電池パックですが、最近は一つの電池パックにセルを10本以上接続することで数十Vの高電圧を実現したリチウムイオンバッテリーが、電動工具や非常用電源、電動アシスト自転車や電動バイクにも用いられています。
関連記事

私たちデクセリアルズはデバイスの進化に欠かせない材料や次世代のソリューションを生み出す、マテリアルメーカーです。
電子部品、接合材料、光学材料をはじめと世界中のパートナーと新しい価値を生み出していきます。
- SHARE
当社の製品や製造技術に関する資料をご用意しています。
無料でお気軽にダウンロードいただけます。
お役立ち資料のダウンロードはこちら
当社の製品や製造技術に関する資料をご用意しています。
無料でお気軽にダウンロードいただけます。
お役立ち資料のダウンロードはこちら