- 光半導体関連
光センサとは何か? 光センサの基礎知識と測距方式ごとの特徴
光センサとは何か? その主な用途
光センサは、光の強度を検知し電気信号に変換する装置です。可視光線だけでなく、人間の目では捉えられない近赤外線などの不可視光線も利用し、ファクトリーオートメーションのほか、セキュリティシステム、自動ドア、スマートフォンの画面輝度調整など、さまざまな場面での検出作業に応用されています。
センサには光センサ以外にも、検出対象に応じて「圧力センサ」「角度センサ」「加速度センサ」などがありますが、光センサが得意とするのは「物体の検出」です。
光センサは、主に「投光素子」と「受光素子」から成り立っています。投光素子が発する光が対象物に当たり、その反射光または透過光の強度を受光素子が捉えることで、物体の存在を検知します。この原理を活用し、工場の生産ラインにおける製品の有無確認、モーターの回転数測定、寸法計測など、人間の目に代わって高精度な検出を行い、品質確認や産業機械の自動化に大きく貢献しています。
光センサの5つの大きな特徴
光センサには以下5つの特徴があります。
- 非接触測定
光センサは物理的な接触なしで対象物を検出します。これにより、測定対象を傷つけることなく測定が可能です。特に繊細な材料や表面、衛生管理が重要な環境での使用に適しています。 また、動いている対象物の検出や、高温・高圧などの過酷な環境下での測定にも有効です。 接触式センサと比べて摩耗や劣化が少なく、長寿命であるという利点もあります。 食品業界、製薬業界、半導体製造など、クリーンな環境を要する分野で広く活用されています。 - 高速応答
光の速度で動作するため、マイクロ秒オーダーの非常に高速な応答が可能です。 この特性により、高速な生産ラインや品質管理システムでの使用に適しています。 例えば、飛行する小さな粒子の検出や、高速で移動する製品の位置決めなどに利用されます。 また、リアルタイムでのフィードバック制御や、高速なカウンティング作業にも適しています。 この高速性は、産業用ロボットの制御や、高速印刷機の紙詰まり検出などにも活用されています。 - 広い検出範囲
光の直進性を利用して、近距離から遠距離まで幅広い範囲での検出が可能です。 レンズやミラーを使用することで、検出範囲をさらに拡大したり、焦点を絞ったりすることができます。 この特性により、小さな部品の検出から大型の物体の位置測定まで、さまざまな用途に対応できます。 また、一つのセンサで広範囲をカバーできるため、設置数を減らしコスト削減にも貢献します。 建築物の侵入検知システムや、大規模な倉庫での物体検知など、幅広い分野で活用されています。 - 多様な検出対象
光センサは物体の有無だけでなく、対象物の色、透明度、反射率、形状などさまざまな特性を検出できます。 この多様性により、製品の品質管理、分類、識別などの複雑なタスクに適しています。 例えば、食品業界での異物検出や、自動車業界での塗装品質チェックなどに利用されます。 また、バーコードやQRコードの読み取りなど、情報の光学的な読み取りにも使用されます。 さらに、光の波長を選択することで、可視光線だけでなく赤外線や紫外線を利用した検出も可能です。 - 環境の影響を受けやすい
光センサは周囲の光条件や粉塵、水滴、振動などの環境要因に影響されやすく、適切な設置や保護が必要です。 特に屋外や工場など、光条件が変化しやすい環境では、誤検出を防ぐための対策が重要です。 これらの影響を軽減するために、フィルターの使用や、センサの設置位置の工夫が行われます。 また、センサ自体の防塵・防水性能を高めたり、温度補償機能を付加したりする対策も取られます。 定期的なメンテナンスや校正も、安定した性能を維持するために重要な要素となります。
光センサの測距方式の違い
次に光センサの測距方式について、主要な方式とその特徴を説明します。まず、大きく分けて「透過型」と「反射型」があり、さらに反射型には4つの方式があります。以下、それぞれについて詳しく解説します。
・透過型
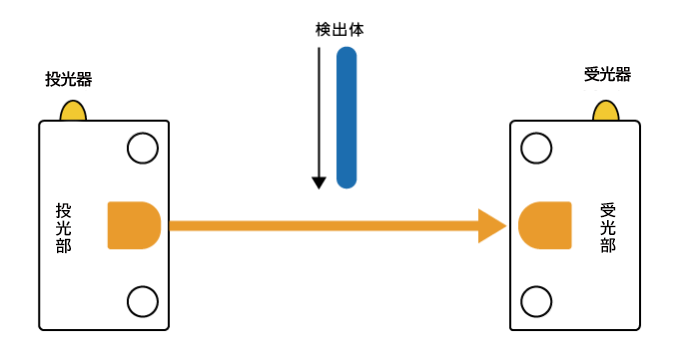
透過型光センサは、投光器と受光器を対向させて配置し、その間を検出対象が通過することで測定を行います。高精度な検出が可能で、背景の影響を受けにくいという特徴があります。また、透明体の検出も可能です。さらに、数十センチの近距離から、数十メートルの長距離の検出にも適しており、動作が安定していることから、さまざまな用途で活用されています。設置には、投光器と受光器を厳密に位置合わせすることが必要なほか、検出エリアが直線的に限定されることにも注意する必要があります。
主な用途:製造ラインでの製品の有無検出、エレベーターのドア安全装置、自動ドアの人体検知など
・反射型
反射型の光センサは、投光器と受光器が同じ側にあり、対象物からの反射光を利用して検出を行います。反射型にはさらに4つの方式があります。
a. 拡散反射型
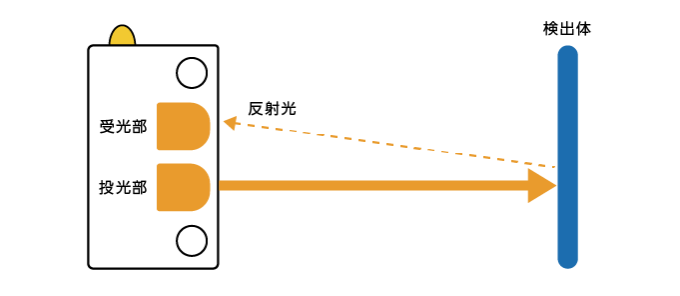
拡散反射型は、検出対象物自体からの反射光を利用して検出を行います。1つの装置ユニットで完結することから設置が容易で、さまざまな形状や材質の物体が検出可能です。検出距離が透過型に比べて短いため、近距離での検出に適しています。また、対象物の色や表面状態によって、検出能力が変化することがあります。
用途:生産ラインでの部品の有無検出、パッケージングラインでの製品検知、ロボットアームの位置決めなど
b. 距離設定型
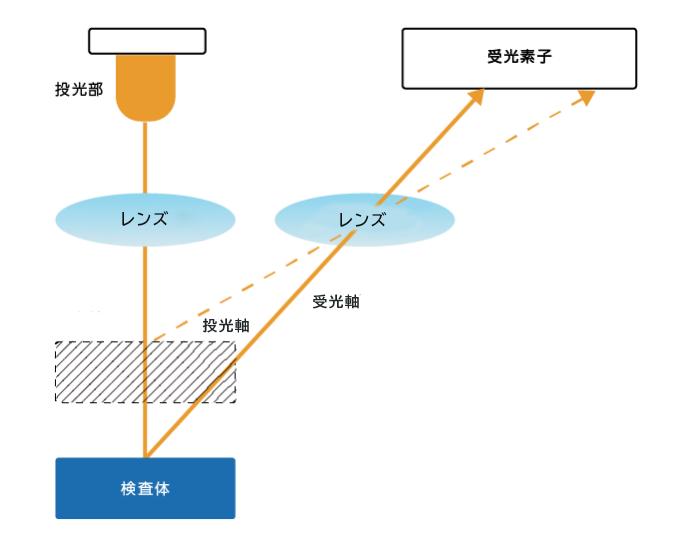
距離設定型光センサは、対象物までの距離を正確に測定し、設定された距離範囲内に対象物が存在するかどうかを判断できるセンサです。このタイプのセンサは、三角測距方式を用いて距離を測定します。センサから特定の角度で光を発射し、検査体にぶつかって反射した光を受光素子で受け止めます。その際に、反射光が受光素子のどの位置に入射したかを検出し、その位置情報と入射角度から三角関数を用いて、検査体との距離を計算します。精度の高い距離測定が可能で、検査体の色や凹凸の影響を受けにくいのが特徴です。
用途:組立ラインでの部品の位置決め、倉庫での在庫管理、自動車の駐車支援システムなど
c. 回帰反射型
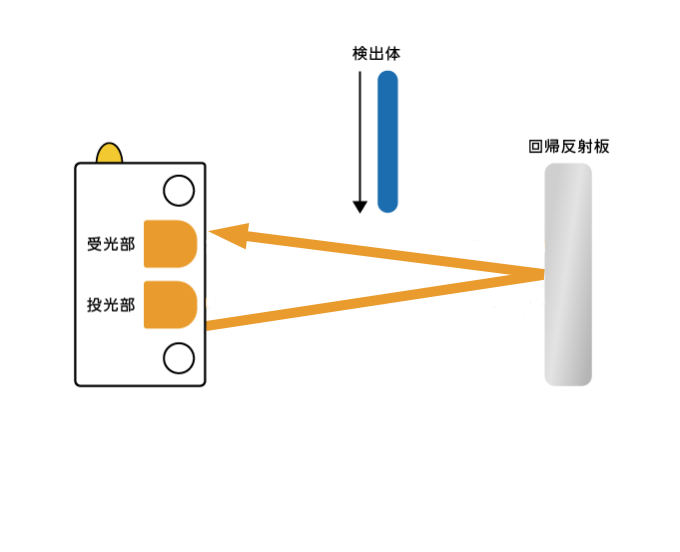
回帰反射型は、専用の反射板(リフレクター)を使用し、その反射板からの反射光が検査体によって遮られることで対象物を検出します。長距離検出が可能で、安定した検出性能を発揮し、小さな物体の検出にも適しているという特徴があります。
用途:工場での大型機械の位置検出、物流センターでの荷物の通過検知、鉄道の踏切制御システム
d. 限定反射型
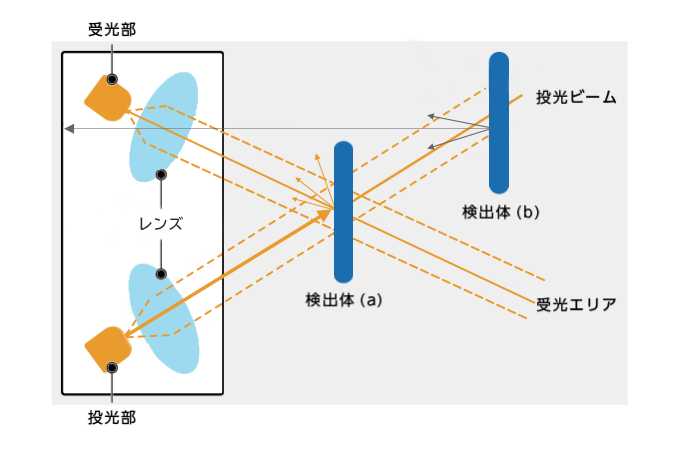
限定反射型は、特定の距離にある対象物のみを検知する方式です。投光部と受光部が別々にあり、それぞれの光軸が斜めに交差するように設置されています。それにより、投光軸と受光軸が交差する特定の範囲(検出エリア)内にある物体からの反射光だけを検出します。こちらのイラストでいえば、検出体(a)は検出できますが、検出体(b)は検出されません。検出エリア外の背景や物体を無視できるため、複雑な環境でも安定した検出が可能です。
用途:コンベアライン上の物体検出など
最適な光センサを選択するために
これらの測距方式は、それぞれ特徴や長所、短所があり、適用される用途によって最適な方式が選択されます。例えば、生産ラインでの一般的な物体検出には拡散反射型が適している一方、長距離での検出や高精度な位置決めが必要な場合は、回帰反射型や距離設定型が選ばれることがあります。
また、最近の技術進歩により、これらの基本的な方式を組み合わせたハイブリッド型のセンサや、レーザーを使用した高精度な測距センサなども開発されています。これにより、より複雑な環境や要求に対応できるようになっています。光センサの選択に当たっては、検出対象の特性(大きさ、形状、材質、色など)、検出距離、周囲環境(光、温度、湿度など)、要求される精度や応答速度などを総合的に考慮する必要があります。また、産業用途では耐久性や信頼性も重要な選択基準となります。
最適な光センサの選択と適切な設置・調整を行うことで、生産性の向上、品質管理の強化、安全性の確保など、さまざまな分野で大きな貢献を果たすことができます。技術の進歩にともない、光センサの性能や機能は日々進化しており、今後もさらなる応用範囲の拡大が期待されています。
関連記事

私たちデクセリアルズはデバイスの進化に欠かせない材料や次世代のソリューションを生み出す、マテリアルメーカーです。
電子部品、接合材料、光学材料をはじめと世界中のパートナーと新しい価値を生み出していきます。
- SHARE
当社の製品や製造技術に関する資料をご用意しています。
無料でお気軽にダウンロードいただけます。
お役立ち資料のダウンロードはこちら
当社の製品や製造技術に関する資料をご用意しています。
無料でお気軽にダウンロードいただけます。
お役立ち資料のダウンロードはこちら