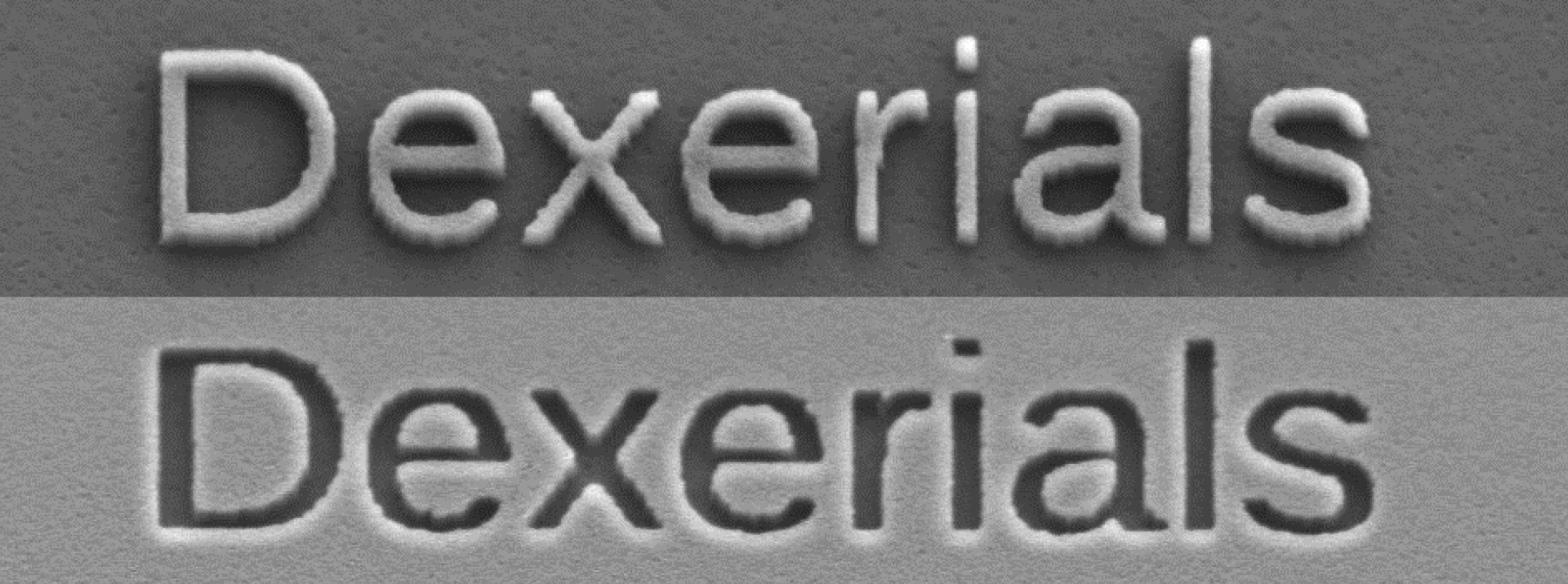- 光学関連
無機偏光板--その技術と特長
偏光とは(偏光板の仕組み)
大画面テレビやパソコンなどの液晶ディスプレイや、ビジネスシーンで活用されるプロジェクターなどの機器を構成する重要な部品の一つに、「偏光板」と呼ばれる光学デバイスがあります。デクセリアルズでは2008年に、耐熱性と耐久性に優れた無機材料による偏光板の発売を始め、光学デバイスビジネスを展開してきました。本稿では、偏光板のはたらきと、当社の扱う最新の無機偏光板の性能について解説します。
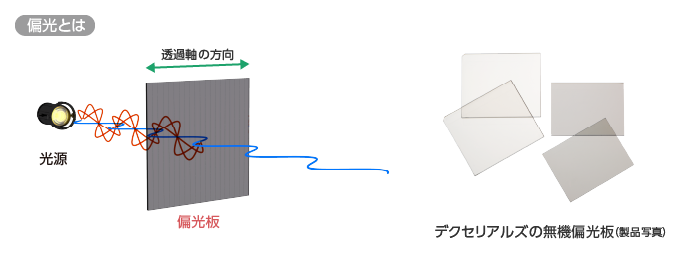
はじめに、「偏光」とは何かを見ていきましょう。ご存知のとおり、光は「電磁波」の一種です。波という文字が示すように、光が進む方向に対して波打ちながら進んでいます。太陽光や月の光、蛍光灯の光など、いわゆる「自然光」と呼ばれる光は、その波の振動がタテ・ヨコ・ナナメ、ランダムに入り混じった状態です。それに対して「偏光」は、波の振動が特定の方向だけに偏っている状態の光を指します。
「偏光板」は、ランダムに振動する光から人工的に「偏光」を作り出すために生み出された光学デバイスです。基材の上に特定の方向に振動する光のみを通すフィルター構造を造形することで、自然光から偏光を取り出すことを可能にします。下記は、偏光していない自然光から偏光板によって垂直成分をカットし、水平成分のみを取り出したときの模式図になります。
プロジェクターの偏光板に求められる性能
プロジェクターに用いられる偏光板も、基本的に液晶ディスプレイと同様の機能を果たしています。一方で、プロジェクター用途であるがゆえに、求められる機能があります。ここでは当社が開発するプロジェクター用無機偏光板の特長と機能について解説します。
高透過:第一に求められるのが、特定の振動の光を「高い率で透過すること」です。偏光板を透過しなかった光は、偏光板に吸収されることで熱へと変化します。プロジェクターの光源に使われるレーザーは液晶ディスプレイのバックライトよりもエネルギーが高いため、熱に変わるエネルギーの量も大きくなり、熱対策が必要となります。なるべく光を有効に活用することが、プロジェクターの省電力化にもつながります。
低反射:偏光板で光が反射してしまうと、筐体の内部でさまざまな方向に光が散乱する「迷光」と呼ばれる現象が起こります。迷光が他の光学部品に入り込むことで、画像が二重に投影される「ゴースト」「二重像」と呼ばれる現象が起こることがあります。そのため、偏光板には低反射であることが求められます。
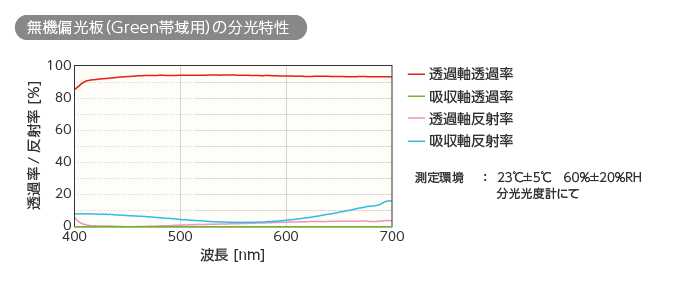
下記のグラフは、当社の無機偏光板(Green帯域用)の波長(横軸)に対する透過率と反射率を示しています。「透過軸透過率」とは、「通したい振動方向の光を透過させる率」のことで、「吸収軸透過率」とは、「通したくない振動方向の光が偏光板を透過させる率」を指します。グラフを見ると、波長550nm付近で90%以上の透過率を示すとともに、吸収軸透過率はゼロに近い値を示し、必要な光の通過を邪魔せず、不要な光はしっかりさえぎっていることが分かります。また、先述の「迷光」と関係するのが「透過軸反射率」と「吸収軸反射率になり、いずれも高いと「迷光」の原因となります。
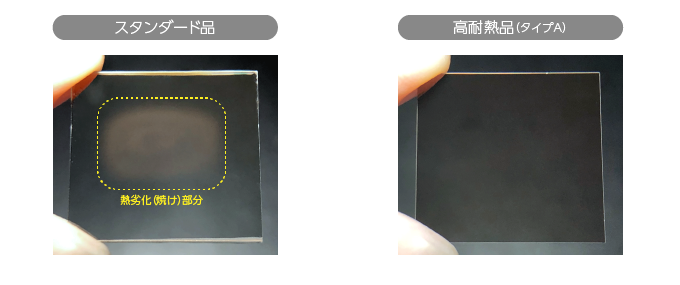
耐熱性:先述のように偏光板を透過しない光は、そのまま偏光板に吸収され、熱へと変化します。すべての光を止めている(画面上では黒を表現)状態が続いているとき、偏光板はかなり高温になり、高輝度化が著しい最近のプロジェクターではその温度が250〜300℃にも達します。それだけの高温に耐える耐熱性が、プロジェクターの偏光板に求められますが、このような高温下では有機材料で構成された一般の偏光板はもちろん耐えられませんが、無機偏光板にとっても過酷な環境と言えます。デクセリアルズでは、市場ニーズに応えるため、より耐熱性を向上させた無機偏光板(高耐熱品)を開発、ラインアップしています。下記の写真はお客さまの実機評価後のスタンダード品と高耐熱品の比較になります。
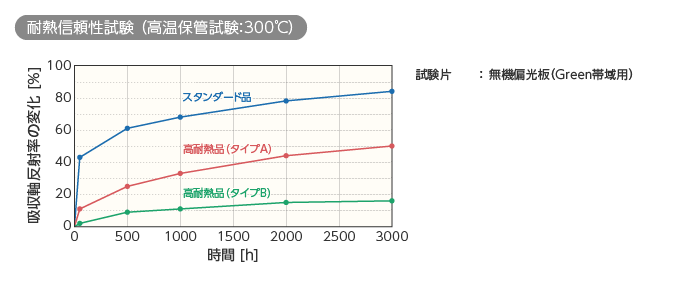
下記のグラフは当社の偏光板について300℃ 3000時間の耐熱性試験を行ったときの、吸収軸反射率の変化を表したものです。高耐熱品は、スタンダード品と比べて時間が経過しても反射率の変化が小さいことが分かります。
耐湿性:プロジェクターの使用環境は、東南アジアなどの高温多湿地域はもちろん、プロジェクションマッピング用途などの屋外にも広がっています。そうした多湿の環境では結露が発生することがあり、無機偏光板に使われている金属材料が腐食することを防ぐ必要があります。デクセリアルズの無機偏光板は、水分に強い保護膜で偏光板をコーティングすることで耐湿性を高めています。
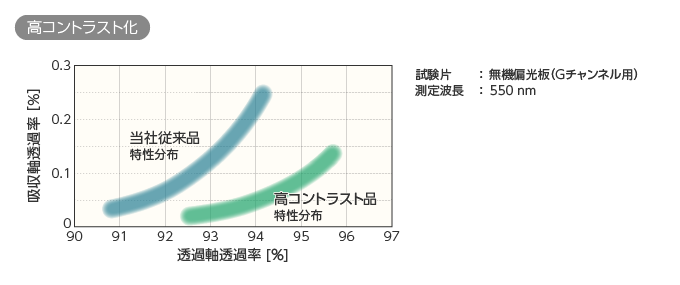
高コントラスト:プロジェクターの映像は、黒はより黒く、白はより白く映るほうが、画面がくっきりと視認でき、画質が向上します。そのためには、コントラスト比を高くする必要があります。コントラスト比を高くするには、偏光板によって「特定の光が通る率を高める」とともに、「それ以外の光は透過させない」ことが大切となります。下記のグラフは、横軸に「透過させたい光の透過率」、縦軸に「透過させたくない光の透過率」をとっており、青いラインが従来品の偏光板、緑のラインが当社が開発した無機偏光板を意味しています。このグラフでいえば、右下に行くほどコントラスト比が高いことを表し、当社の偏光板の性能が高いレベルにある事が分かります。
革新を続けるデクセリアルズの偏光板
上記のコントラスト比は、プロジェクターの画質に直結する指標ですが、10年ほど前までは透過軸透過率が88%ぐらいの無機偏光板が一般的でした。デクセリアルズでは基材の材料や、基材の上に造形する偏光膜の構造を工夫することで性能を高め続けています。レーザー光源を用いるプロジェクターの需要は拡大を続けており、当社ではこれからも各種の無機偏光板のラインアップによって、お客さまの幅広いニーズに応えてまいります。
関連記事

私たちデクセリアルズはデバイスの進化に欠かせない材料や次世代のソリューションを生み出す、マテリアルメーカーです。
電子部品、接合材料、光学材料をはじめと世界中のパートナーと新しい価値を生み出していきます。
- SHARE
当社の製品や製造技術に関する資料をご用意しています。
無料でお気軽にダウンロードいただけます。
お役立ち資料のダウンロードはこちら
当社の製品や製造技術に関する資料をご用意しています。
無料でお気軽にダウンロードいただけます。
お役立ち資料のダウンロードはこちら