- Elemental Technologies
New “flexible mold” technology for microstructure formation
Contents
Dexerials’ new Flexible Mold technology
Dexerials has established technology for laying down microstructures ranging from several hundred nanometers to several hundred micrometers over hundreds of meters on base materials such as films by combining “roll-to-roll technology” and “nanoimprinting.” By applying this technology, we are now developing a flexible mold technology that uses a flexible film as a mold for microstructures to transfer microstructures to a wide variety of materials and shapes over a large area at a low cost.
This article describes the flexible mold technology and its potential applications.
Basic knowledge of roll-to-roll method
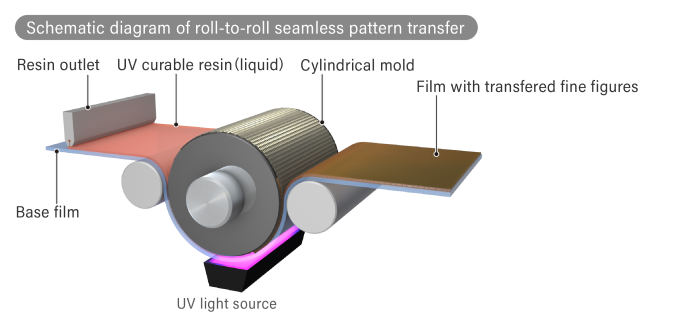
First, we would like to briefly explain Dexerials’ proprietary roll-to-roll method of manufacturing films with microstructures, which is the basis of this technology. In this method, the original shape of the microstructure to be transferred is engraved on the surface of a cylindrical base material made of metal or glass, called a master plate, using precision machining using diamond or other cutting tools or lithographic processing using laser imaging.

In the next process, as shown in the illustration below, UV-curing resin is applied to the surface of the rolled film base material while feeding it from left to right.
The microstructure is then transferred onto the film (imprinting technology) by irradiating it with UV light while pressing it against a cylindrical mastering plate with microfabrication. The structure transferred onto the film base material is the inverted shape of the mold on the mastering plate.
With this technology, Dexerials manufactures and sells “Moss Eye Type Anti-Reflective Film” with excellent low reflection and high transparency, and “Diffusion Microlens Array (DMLA)” that enhances visibility in automobile head-up displays.
Differences from common imprinting techniques
Dexerials’ R&D group is applying this technology to develop a technology for nanoimprinting fine patterns on the surface of substrates other than films (glass and plastic, flat and curved surfaces). This is a new technology we call “flexible molding.
Here, we will explain the single-wafer imprinting process, widely used in imprinting (in which substrates on a board are processed one at a time). In single-wafer imprinting, a plate base material is first fabricated by photolithography and machining (cutting). In some cases, this is used directly as a mold, while in other cases, a replica is made from the master plate and used as a mold.

How to make and use flexible molds
To solve the above issues, Dexerials has developed a flexible mold technology that mass-produces replica molds in film form by combining the technology for producing cylindrical masters and the roll-to-roll imprinting method. On the surface of the produced film, replica shapes that serve as molds for microstructures are laid down and given a special mold release treatment (a treatment that makes it easier to peel off from the mold).

Transfer of microstructure to substrate by flexible mold
The surface of the flexible mold is covered with microstructure molds. As shown in the illustration below, ultraviolet (UV)-curable resin is applied to the glass substrate on which the microstructure is to be transferred, the flexible mold is pressed onto it, and the resin is hardened by UV irradiation. The flexible mold is pre-treated with a mold release to make it easy to peel off, so the microstructure is transferred to the resin once the mold is peeled off.

Single-wafer imprinting technology using flexible molds
By combining the above flexible mold with the imprinting materials that Dexerials is developing, it will be possible to transfer and form microstructures on non-film substrates such as glass and plastic substrates, even over large areas, since flexible molds are soft and bendable, nanoimprinting on the surface of curved materials becomes possible, which is a major advantage over the conventional single-wafer process.
In addition, the roll-to-roll production method makes it possible to produce large-area flexible molds at low cost and with high efficiency. Microfabrication of silicon wafers, glass substrates, plastic substrates, and other substrates can be applied to various devices that will continue to become more multifunctional. We will continue pursuing the development potential of flexible mold technology and work with our customers to create unprecedented new value.
- SHARE
 Back to top
Back to top  Contact us
Contact us